Metadata
Overview
Teaching: 0 min
Exercises: 30 minQuestions
How are my data published?
What metadata are required for publishing?
Objectives
Showing data publishing pipeline
Introducing the IPT
Introduction to EML
Integrated Publishing Toolkit
The Integrated Publishing Toolkit (IPT) is an open-source web application developed and maintained by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) for publishing biodiversity data. The IPT makes it easy to share four types of biodiversity-related information:
- primary taxon occurrence data
- sampling event data
- general metadata about data sources
- taxon checklists
GBIF maintains a very detailed IPT manual The Croatian IPT is available here.
The requirements for publishing data through your node IPT are that:
- you have contacted the node to ensure the data are a good fit
- the data follows Darwin Core (DwC) and Ecological Metadata Language (EML)
- includes the required Darwin Core and EML metadata elements
Presentation
Ecological Metadata Language (EML)
Both OBIS and GBIF use Ecological Metadata Language (EML) as the metadata standard associated with the data. For the purposes of this workshop we will not dive into the world of EML. However, we should note that when publishing your data through the IPT, the IPT helps you create an EML file as part of the Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A). As such, if you publish your own data through the IPT, there is no need for innate knowledge on the EML format. But there are a minimum required number of fields that would need to be filled out in the IPT: title, abstract, citation, and several contacts.
More information on EML can be found at the EML standard page, and in the bio data guide. There are also a number of R packages for working with EML, reviewed here.
Tip
Try to collect as much of this information as possible before and during the Darwin Core alignment process. It will significantly reduce the amount of time it takes to load the data into the IPT.
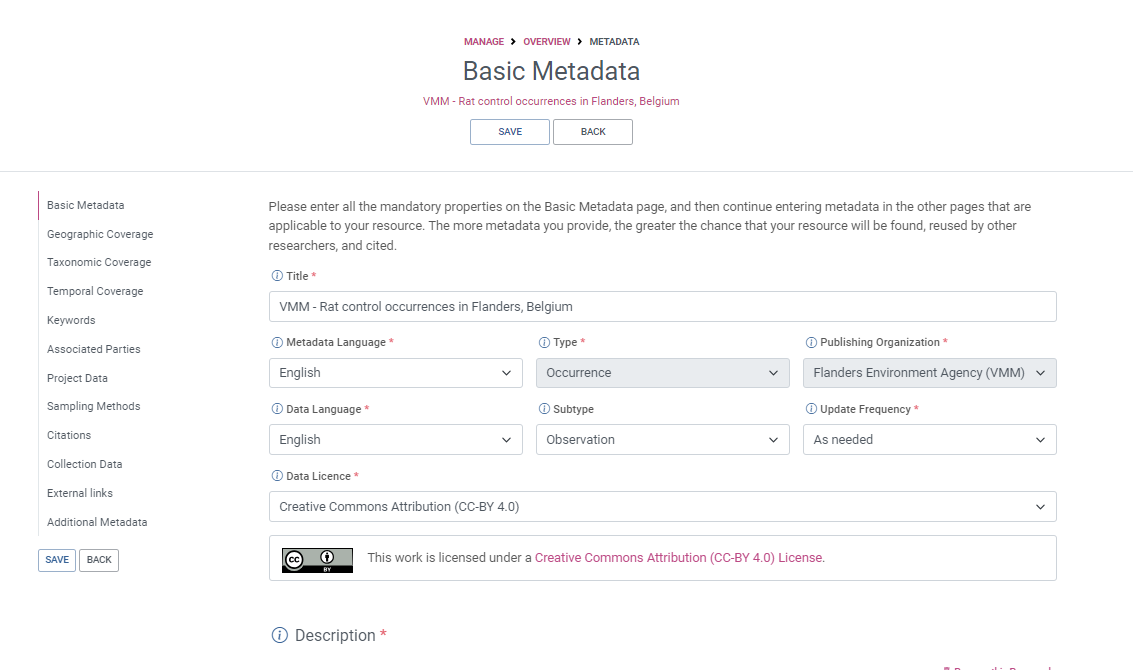
Required EML metadata fields for sharing to GBIF
Best practices for these fields are explained in detail in the GBIF IPT user manual_Resource metadata Simply use the IPT’s built-in metadata editor to populate the metadata.
| IPT/EML Fields | Definition | Comment |
|---|---|---|
title |
A good descriptive title is indispensable and can provide the user with valuable information, making the discovery of data easier. | The IPT also requires you to provide a Shortname. Shortnames serve as an identifier for the resource within the IPT installation and should be unique, descriptive and short (max. 100 characters). Spell out acronyms in Title but they are ok to use in the shortname. |
description |
The abstract or description of a dataset provides basic information on the content of the dataset. The information in the abstract should improve understanding and interpretation of the data. | |
license |
The licence that you apply to the resource. The license provides a standardized way to define appropriate uses of your work. | Must use CC-0, CC-BY, or CC-BY-NC. Description of the licenses can be found here. |
resource Contact(s) |
The list of people and organizations that should be contacted to get more information about the resource, that curate the resource or to whom putative problems with the resource or its data should be addressed. | Last name, Postition, and Organization are required, helpful to include an ORCID and a contact method like email or phone number. |
resource Creator(s) |
The people and organizations who created the resource, in priority order. The list will be used to auto-generate the resource citation (if auto-generation is turned on). | |
metadata Provider(s) |
The people and organizations responsible for producing the resource metadata. | |
publishing organisation |
The organization who publishes the data i.e. the data publisher |
Other EML fields to consider
| IPT/EML Fields | Definition | Comment |
|---|---|---|
Bounding Box |
Farthest North, South, East, and West coordinate. | |
Geographic Description |
A textual description of the geographic coverage. | |
Temporal Coverage |
This can either be a Single Date, Date Range, Formation Period, or Living Time Period. | |
Study Extent |
This field represents both a specific sampling area and the sampling frequency (temporal boundaries, frequency of occurrence) of the project. | |
Sampling Description |
This field allows for a text-based/human readable description of the sampling procedures used in the research project. | The content of this element would be similar to a description of sampling procedures found in the methods section of a journal article. |
Step Description |
This field allows for repeated sets of elements that document a series of methods and procedures used in the study, and the processing steps leading to the production of the data files. These include e.g. text descriptions of the procedures, relevant literature, software, instrumentation and any quality control measurements taken. | Each method should be described in enough detail to allow other researchers to interpret and repeat the study, if required. |
citation |
To ensure your dataset gets cited the way you want |
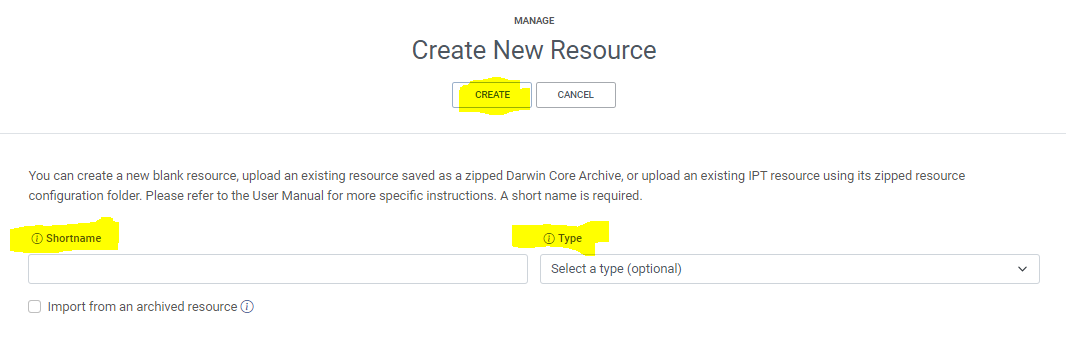
Exercises 1: Create an ‘imaginary’ dataset in the Croatian IPT
- Go to the Croatian ‘test’ IPT instance on ipt.bioportal.hr
- Login to the ‘IPT’ instance, you can login with your emailaddress and
WelcomCroMent- Click on
manage resources- Click on
Create Newand choose your the type of your dataset (here chooseoccurrence)- Give a shortname for your resource,
the shortname serves as an identifier for the resource and will be used as a parameter in the url- Click on
CreateSolution
- You have created your first resource on the IPT
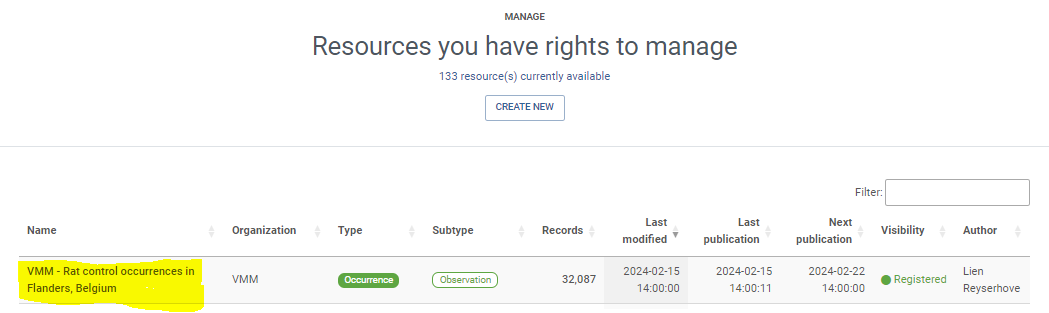
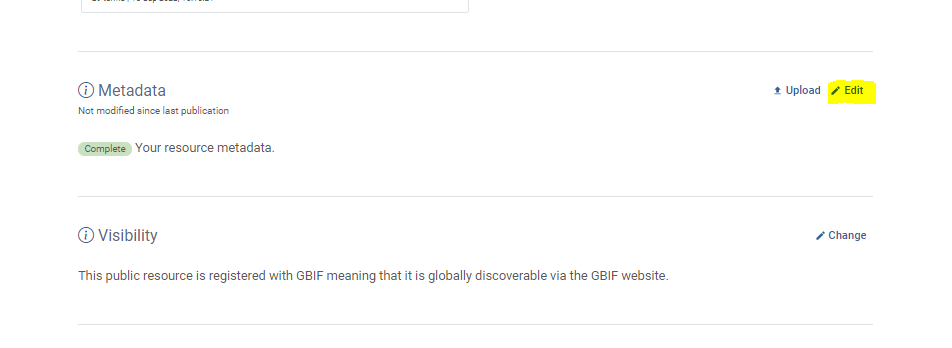
Exercises 2: Create ‘imaginary’ metadata for your dataset
- Go to the Croatian ‘test’ IPT instance
- Login
- Click on
Manage resources- Click on your ‘imaginary’ dataset
- Click on
editin theMetadatasection- Complete the Metadata wizzard, starting with providing a tittle for your dataset
Solution
- Congratulations, you did add metadata in your dataset
Exercises 3: Link and map your ‘imaginary’ dataset in the Croatian IPT
- Go to the Croatian ‘test’ IPT instance
- Login
- Click on
Manage resources- Click on your ‘imaginary’ dataset
- Click on
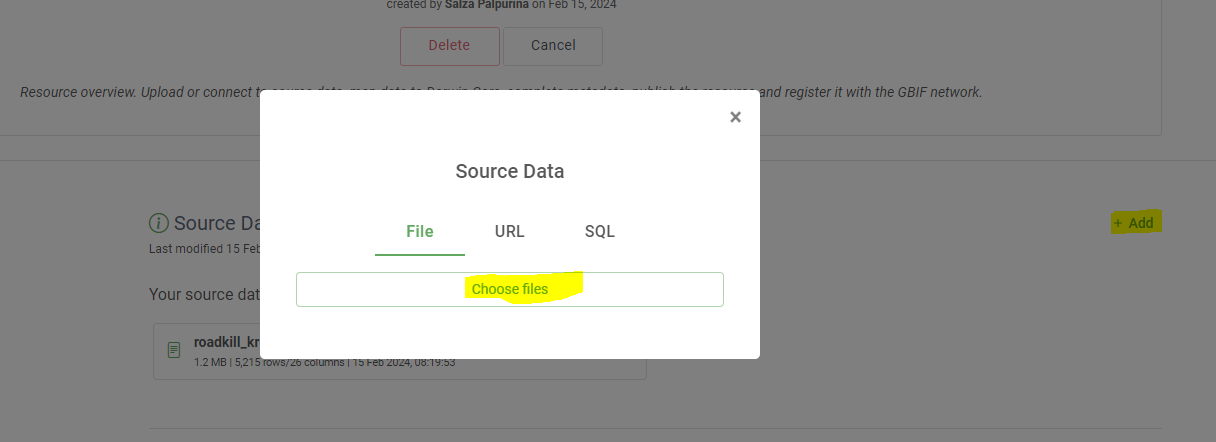
addin theSource datasection- Choose your source data:
- A File (Choose
occurrencememo.csvif you don’t have an ‘imaginary’ dataset- An url
- An SQL statement
- Click on
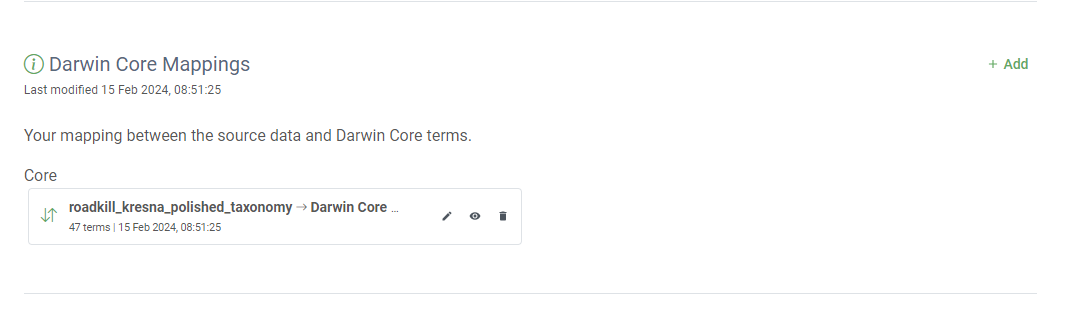
addin theDarwin Core Mappingssection- CLick again on
add, make sure Darwin Core Occurrence is selected- Select the source ‘occurrencememo
and clicksave`- Your data is automapped to Darwin Core, you can click on
saveSolution
- Congratulations, you or you nodemanager can publish this dataset after validation
Datapapers
Tip
- In some cases you’ll want to ensure the values are representative of the entity you are reporting.
- For example,
individualCountshould be an integer. So, checking that column for integer values would be good.
Key Points
The IPT is a well-documented and flexible system for publishing data to GBIF (and OBIS)
Some Darwin Core and Ecological Metadata Language fields are required for publishing to GBIF (and OBIS).
Strive to write more than the minimal metadata